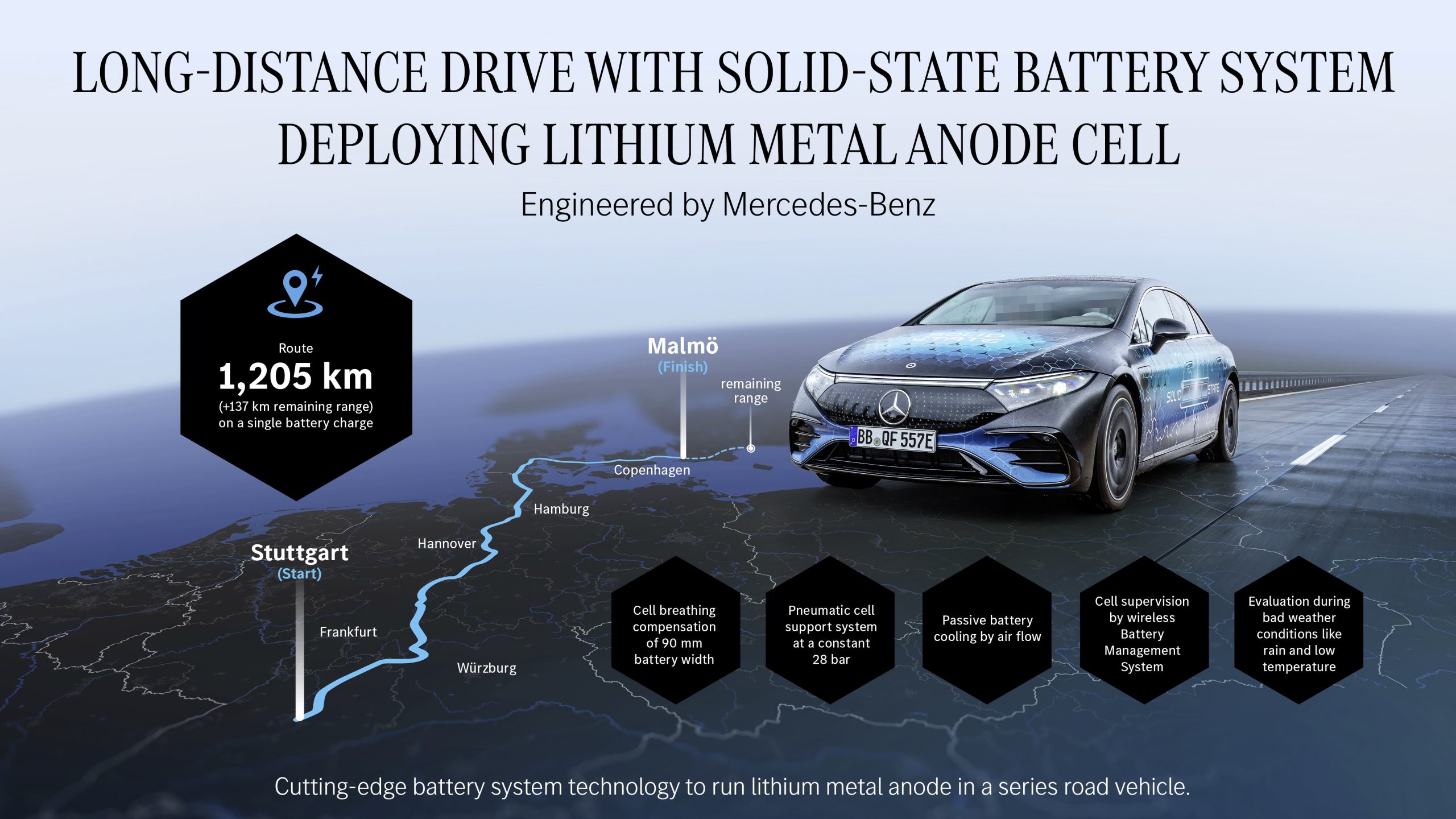
Long-distance test successfully completed: EQS with solid-state battery covers 1,205 km on a single charge


- Mercedes-Benz continues real-world testing of solid-state battery technology
- No charging stops across three countries: From Stuttgart, Germany via Denmark to Malmö, Sweden
- Total distance covered: 1,205 km without recharging. Remaining range: 137 km
- Formula 1 technology: Solid-state battery developed with Mercedes-AMG High Performance Powertrains (HPP) and cells from U.S.-based solid-state cell manufacturer Factorial Energy
Stuttgart. Mercedes-Benz sets new benchmarks in electric mobility with an extraordinary demonstration drive, impressively showcasing the potential and everyday usability of a future battery technology: A lightly modified EQS test vehicle was used for the journey. It was equipped with a lithium-metal solid-state battery.
At the end of August, the vehicle completed the 1,205-kilometer trip from Stuttgart in Germany to Malmö in Sweden. Remarkably, it did so without a single charging stop. This real-world achievement proves that the technology performs not only in the lab but also on the road.
The EQS surpassed the previous record set by the Vision EQXX on its Stuttgart–Silverstone route by three kilometres. It arrived in Malmö with an impressive remaining range of 137 km, too. This combination of long range, efficiency, and technological maturity marks a milestone for solid-state battery development and highlights its potential for future production vehicles.
As the inventor of the automobile, Mercedes-Benz once again underscores its ambition to actively shape the future of mobility through this pioneering achievement.
Real-world validation
Following the announcement of road testing in February, the drive from Stuttgart in Germany to Malmö in Sweden was part of a comprehensive validation program for solid-state battery technology at Mercedes-Benz. In addition to digital simulations and testing at state-of-the-art facilities in Stuttgart-Untertürkheim and Sindelfingen, the vehicle and battery are being tested under real-world conditions on public roads. The goal is to assess overall vehicle performance across different climate zones and route profiles and accelerate the path to series production. The recent trip to Malmö adds a real long-distance scenario to this testing program.
The route followed highways A7 and E20 through Germany and Denmark to Malmö, Sweden. The optimal route was calculated using Electric Intelligence, factoring in topography, traffic, ambient temperature, and energy needs for heating and cooling — without using ferries.
“The solid-state battery is a true gamechanger for electric mobility. With the successful long-distance drive of the EQS, we show that this technology delivers not only in the lab but also on the road. Our goal is to bring innovations like this into series production by the end of the decade and offer our customers a new level of range and comfort.”
Markus Schäfer, Member of the Board of Management of Mercedes‑Benz Group AG, Chief Technology Officer, Development & Procurement
Technology Background
The solid-state battery system was developed in close collaboration with Mercedes-AMG High Performance Powertrains (HPP), the Formula 1 technology centre of the Mercedes-Benz Group in Brixworth, UK. The lithium-metal cells used in the vehicle come from U.S.-based manufacturer Factorial Energy and are based on FEST® technology (Factorial Electrolyte System Technology).
To support the cells during the volume changes typical of this technology and to ensure the necessary contact pressure on the cells, the solid-state battery is equipped with pneumatic actuators. These actuators respond to the changes in cell volume during charging and discharging, thereby ensuring the flawless operation of the battery over time. The usable energy content of the battery was increased by 25%, while the weight and size of the battery remain comparable to the standard EQS battery. Additional weight and energy efficiency is achieved through passive airflow cooling.
If you enjoyed this article, be sure to follow us on Microsoft Start.










