How Long Should A Car Battery Last?


Most drivers expect their car to start without hesitation, but the battery behind that reliability does not last forever. On average, a standard car battery lasts about three to five years, while newer types such as AGM or lithium-ion can last longer depending on use and conditions. Knowing this range helps set realistic expectations and prevents being caught off guard by a sudden failure.
Battery life depends on more than just time. Climate, driving habits, and vehicle features all play a role in how long a battery performs effectively. Short trips, extreme temperatures, and high electrical demand can shorten its lifespan, while regular maintenance and proper charging can extend it.
Understanding how long a battery should last, what shortens its life, and the signs of failure makes it easier to plan replacements before problems arise. This article explains the typical lifespan, key factors that influence performance, warning signs to watch for, and what steps to take when a battery can no longer hold a charge.
Average Lifespan of a Car Battery
Car batteries do not last indefinitely. Their service life depends on factors such as climate, driving patterns, battery type, and maintenance practices. Understanding these differences helps drivers plan for replacement before failure occurs.
Typical Battery Life Expectancy
Most 12-volt lead-acid batteries last between 3 to 5 years under normal use. In cooler climates, some reach closer to 5 years, while in hot regions they often last closer to 3 years. Heat accelerates chemical breakdown inside the battery, reducing its lifespan.
Short trips also limit charging cycles, which can leave the battery undercharged. Vehicles left unused for long periods experience self-discharge, which further shortens service life. Using a maintenance charger during storage can help extend battery longevity.
It is common for warranties to last about 3 years with full replacement coverage. A battery might function beyond that period, but reliability decreases significantly after year four. Drivers should begin testing their battery annually once it reaches the three-year mark.
How Battery Type Affects Longevity
Not all car batteries age at the same rate. Conventional lead-acid batteries are the most common and usually last 3 to 5 years. They are affordable but more sensitive to deep discharges and extreme temperatures.
Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) batteries often last slightly longer, sometimes 4 to 6 years, because they handle repeated charging cycles better. They are used in vehicles with stop-start systems or high electrical demands. Proper charging is essential, as overcharging can shorten their life.
Lithium-ion batteries, found in some hybrid and electric vehicles, have a different lifespan profile. These can last 8 to 10 years or more, but they require advanced management systems to regulate charging and temperature. Their replacement cost is significantly higher than traditional 12-volt batteries.
Choosing the correct type specified by the manufacturer ensures the charging system matches the battery’s requirements. Installing the wrong type can reduce longevity and cause electrical issues.
When to Replace Your Car Battery
A car battery should be replaced once it can no longer reliably hold a charge or when test results show significant deterioration. Warning signs include slow engine cranking, dashboard warning lights, or dim headlights at idle.
Even without obvious symptoms, replacement is recommended around the 3 to 5 year range for lead-acid batteries. Waiting longer increases the chance of sudden failure, which can leave a driver stranded.
Routine inspections help identify early issues. Checking for corrosion on terminals, ensuring tight connections, and confirming the hold-down bracket is secure all contribute to longer service life.
Professional battery testing provides a clear measure of remaining capacity. If results show the battery is weak, scheduling a replacement before complete failure avoids unexpected breakdowns.
Key Factors That Influence Car Battery Life
Car battery life depends on several conditions that directly affect how long it can reliably hold a charge. Temperature, driving patterns, upkeep, and the health of the charging system all play a role in determining whether a battery lasts closer to three years or stretches to five or more.
Environmental Conditions and Climate
Temperature extremes shorten a car battery’s lifespan. High heat accelerates chemical reactions inside the battery, which increases wear and speeds up fluid evaporation. In hot climates, batteries often last closer to three years.
Cold weather presents a different problem. Low temperatures reduce the battery’s ability to deliver current, making engine starts harder. A weak battery that might work in summer can fail quickly in freezing conditions.
Placement under the hood adds stress because heat from the engine raises surrounding temperatures. Some manufacturers move batteries to the trunk or under seats to reduce exposure. This design helps limit degradation from prolonged high heat.
Drivers in regions with seasonal extremes should expect shorter service life and plan for testing once the battery reaches three years of use.
Driving Habits and Usage Patterns
Frequent short trips prevent a car battery from fully recharging. Starting the engine uses a large burst of power, and if the alternator does not have enough time to restore the charge, the battery remains undercharged. Over time, this reduces its capacity.
Vehicles left parked for long periods also face problems. Batteries naturally self-discharge, and without regular use or a maintenance charger, they can fall below healthy charge levels. Once deeply discharged, recovery is limited, and lifespan is shortened.
Longer drives at steady speeds give the alternator time to recharge the battery fully. Cars used daily on mixed routes usually see better battery life than those driven rarely or only for very short distances.
Battery Maintenance and Care
Proper maintenance extends service life. Corrosion on battery terminals increases resistance and reduces charging efficiency. Cleaning connections and keeping them tight prevents unnecessary strain on the charging system.
Securing the battery with hold-down hardware prevents vibration damage. Excessive movement inside the case can cause internal plates to break down, leading to early failure.
Regular testing helps identify weakening batteries before they fail. Once a battery reaches three years of age, annual checks can provide a clear picture of its condition. Using a charger during long storage periods also helps maintain a healthy state of charge.
Electrical System Health
A malfunctioning charging system shortens battery life. Undercharging leaves the battery in a constant low state, while overcharging causes overheating and fluid loss. Both conditions accelerate aging.
Modern vehicles with absorbent glass mat (AGM) batteries require precise charging control. If the alternator or voltage regulator fails, the battery can deteriorate much faster than expected.
Electrical accessories that draw power while the car is off, such as alarms or aftermarket devices, also contribute to discharge. Identifying and correcting parasitic drains prevents unnecessary wear.
Routine inspection of the alternator, voltage regulator, and wiring ensures the battery receives a stable charge. A healthy electrical system directly supports longer and more consistent battery life.
Warning Signs of Battery Failure
A weakening car battery often shows clear signs before it completely fails. Common indicators include slow starting, dim or inconsistent electrical performance, and visible corrosion around the terminals. Recognizing these symptoms early helps avoid a situation where the car won’t start at all.
Slow Engine Crank and Hard Starts
One of the most frequent early warnings of battery failure is a slow engine crank. When the driver turns the key or presses the start button, the engine may turn over sluggishly before finally starting. This indicates the battery is struggling to supply sufficient current to the starter motor.
In colder weather, slow cranking becomes more noticeable because batteries lose capacity in low temperatures. A healthy battery should allow the engine to start quickly even in cold conditions. If the engine consistently hesitates or requires multiple attempts to start, the battery is nearing the end of its service life.
Repeated hard starts also place strain on other components, such as the starter and alternator. Testing the battery voltage with a multimeter can confirm whether the issue is due to weak charge or internal deterioration.
Dim Headlights and Electrical Issues
Dimming headlights are another clear indication of a failing car battery. Headlights that appear weaker than usual, especially when idling, suggest that the battery cannot maintain steady voltage output. A properly functioning battery should support consistent brightness regardless of driving conditions.
Other electrical issues often appear alongside dim headlights. Dashboard lights, power windows, and infotainment systems may perform erratically if the battery is weakening. In some cases, the battery warning light on the dashboard will illuminate, signaling a charging or battery-related problem.
If multiple electrical systems show reduced performance, the issue is often linked to insufficient battery power rather than isolated component failures. Testing the battery load and checking alternator output can help confirm the source of the problem.
Corrosion and Battery Terminal Problems
Corrosion around battery terminals is a common physical sign of battery trouble. It usually appears as a white or bluish deposit on the metal posts or cable connections. This buildup interferes with the flow of electricity, leading to poor conductivity and starting issues.
Loose or dirty terminals can also mimic symptoms of battery failure, such as slow cranking or intermittent electrical faults. Cleaning the terminals with a proper brush and tightening the connections can sometimes restore normal operation.
If corrosion returns quickly after cleaning, it often indicates the battery is venting gases due to internal damage or overcharging. In such cases, replacement is usually necessary to prevent recurring problems and avoid complete loss of starting power.
What to Do When Your Car Battery Fails
A failed car battery can leave a vehicle unable to start, but drivers have two main solutions: restoring temporary power with a jump start or replacing the battery entirely. Both steps require careful handling to avoid damage to the vehicle or injury.
How to Jump Start a Dead Battery
Jump starting provides temporary power by connecting a weak battery to a charged one. The process requires jumper cables and another vehicle with a working battery. Both cars should be turned off before connecting the cables.
Attach the red cable to the positive terminal of the dead battery, then to the positive terminal of the good battery. Next, connect the black cable to the negative terminal of the good battery. The final black clamp should attach to an unpainted metal surface on the disabled car, away from the battery.
Start the working vehicle first, then attempt to start the car with the dead battery. After the disabled car starts, let it run for at least 15–20 minutes to allow the alternator to restore some charge. Disconnect cables in reverse order. If the car fails to hold a charge, the battery likely requires replacement.
Steps for Safe Battery Replacement
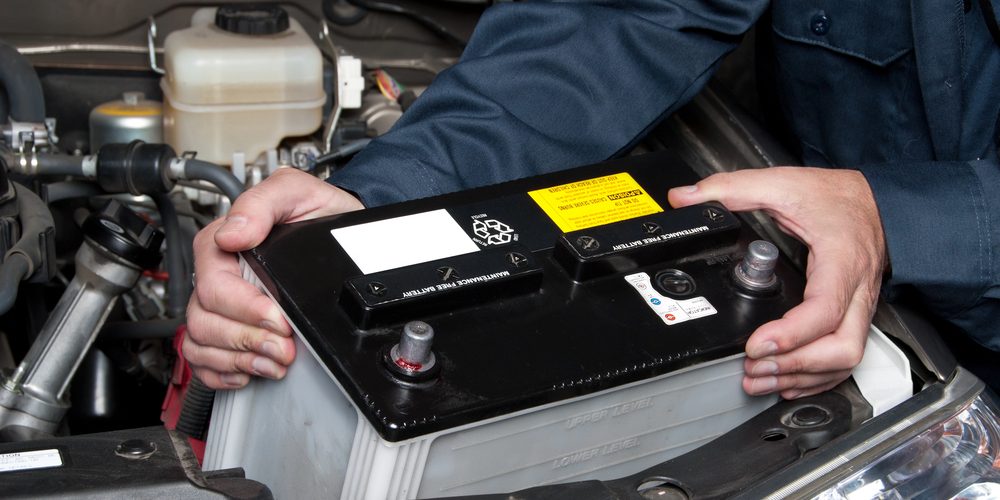
If a battery no longer charges or shows signs of damage such as bulging or leaking, replacement is required. Begin by turning off the engine, setting the parking brake, and wearing protective gloves and glasses.
Disconnect the negative terminal first to reduce the risk of sparks, followed by the positive terminal. Remove any securing brackets and lift the old battery out carefully, keeping it upright to avoid spills.
Place the new battery into the tray, reconnect the positive terminal first, then the negative. Tighten all connections securely and confirm the battery is stable. Old batteries should be taken to an auto parts store or recycling center, as they contain hazardous materials that must be disposed of properly.
After installation, check that the vehicle starts smoothly. If electrical issues persist, the problem may involve the alternator or another part of the charging system.
If you enjoyed this article, be sure to follow us on Microsoft Start.